Battery Instructions
Purchase only a battery with technology and performance that match your vehicle’s requirements!
Otherwise, the battery may be overloaded and its service life reduced!
Within 10 days of purchase, it is mandatory to check the charging voltage of the electric relay at a Rombat partner service center (where available) or at a RAR-authorized service center in locations without a Rombat partner.
The voltage must be within 14 - 14.4 V. If the charging voltage is outside this range, please correct the issue. The certificate becomes valid only when the voltage is correct and noted accordingly.
Charging voltage check is free of charge both at the time of purchase and during the warranty period, at service centers authorized by Rombat and listed in the warranty certificate.
Battery Storage and Maintenance
Batteries delivered with electrolyte should be stored in closed, dry rooms with proper ventilation, temperatures between 5 and 30°C, and relative humidity below 80%, away from heat sources and sunlight. After a maximum storage or inactivity period of:
Batteries must be recharged following the method described in the "Recharging Procedure" section. Storage above 30°C significantly reduces the maximum allowed storage period without recharging. In such cases, the battery voltage must be checked monthly and recharged if it drops below 12.5V.
We recommend battery installation in an authorized service center
Correct installation involves the following steps:
Recommendation:
If one of the batteries fails, both should be replaced!
Disconnect all electrical consumers
Clean the battery terminal and cable lug contact surfaces of oxides until a metallic shine appears
Secure the lugs firmly on the terminals without causing mechanical damage
Only use proper cable lugs for good electrical contact
Disconnection order: first the ground (negative) terminal, then the positive terminal
Connection order: first the positive terminal, then the ground (negative) terminal
In vehicles with 24VDC power systems, both series-connected batteries must be structurally identical, functional, and equally charged (same voltage and electrolyte density)
It is strictly forbidden to connect 12V consumers directly to the terminals of either battery in 24VDC systems
Use a 24VDC/12VDC converter to power such consumers
Usage
We recommend battery checks at the beginning of the cold season, free of charge at any partner service center.
These are maintenance-free batteries; any intervention in the battery construction is prohibited.
Also, check that the vent holes in the caps are not blocked.
If overcharging is observed (indicated by high electrolyte consumption or drop in level), or undercharging (voltage below 12.5V and electrolyte density below 1.25g/cm³), check the vehicle's electrical system (regulator relay, alternator) and recharge the battery promptly.
City driving with frequent starts and short trips (e.g., taxis) can drain the battery faster, even if the system is working properly.
Never leave a discharged battery (under 12V and 1.2g/cm³) at temperatures below 0°C—electrolyte may freeze and damage the plates! Relay voltage must be maintained at (14.2 ± 0.2 V).
Avoid prolonged use of batteries under 70% charge—it leads to capacity under-dimensioning and overload failure (warranty void).
Any time the battery is accidentally discharged during vehicle standby (engine off), eliminate the cause and immediately check the battery’s charge state, taking necessary action (see "Recharging Procedure"). Keep the battery clean and dry. Dust buildup on the battery top can cause self-discharge in standby, leading to battery overload.
Battery Recharging Procedure
Recharge using a charger any battery in one or more of the following conditions:
Accidentally discharged battery (below 75%)
Stored battery at the end of the storage interval defined in the "Storage" section
Discharged battery claimed as defective, before visiting a service center
Charging can generally be performed using any commercial DC charger capable of delivering: 13.5V ≤ Output Voltage ≤ 16.5V and 4A ≤ Output Current ≤ 25A
Typically, charging is done with a current of approx. (5–10)% of Cn (A), until uniform gas release occurs and electrolyte density stabilizes around 1.28 ± 0.01 g/cm³
Toward the end of charging, terminal voltage reaches 15.80–16.50V at 25°C (in charger mode). During charging, battery caps must be removed. Recharging is best done in specialized workshops.
Warning:
For AGM or GEL batteries, charging voltage must remain within 14.4V–14.8V. Do not exceed this limit to avoid overcharging!
The table below shows the indicative battery charge level and open circuit voltage relative to electrolyte density (25°C)
High Risk
Risk
Alert
Acceptable
Charge Level (%)
25
50
75
100
Open Circuit Voltage (V)
12
12.3
12.55
12.8
Electrolyte Density (g/cm³)
1.20
1.20
1.25
1.28
Attention Users
- Batteries must be transported, stored, and installed in their normal upright position to avoid electrolyte leakage!
- Strictly avoid open flames or sparks near batteries installed on a vehicle or undergoing recharging—RISK OF EXPLOSION!
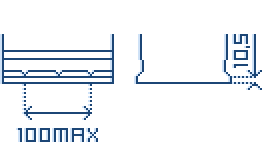
B00 Bottom Hold Down
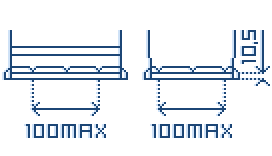
B01 Hold Down
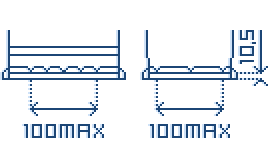
B03 Hold Down
B13 Hold Down
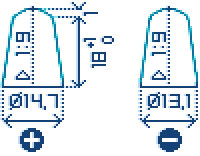
Terminal 1
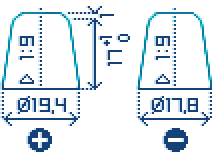
Terminal 3
Mounting Diagram 1
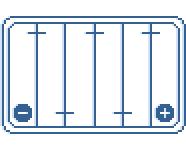
Mounting Diagram 2
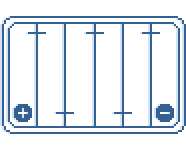
Mounting Diagram 3
Mounting Diagram 4
Read the instructions
Avoid contact with eyes
No open flames, sparks, or smoking
Keep out of reach of children
Sulfuric acid can cause blindness or burns
Explosion hazard
End-user information
Prevent battery waste by encouraging sustainable practices as follows:
- Buy only what you need;
- Choose batteries from companies that promote battery recycling, offer take-back programs, and use recycled materials in production;
- Never throw batteries in the trash; hand them over at designated collection points.
![]() Risks and safety measures
Risks and safety measures
Batteries contain hazardous materials, for example lead (lithium):
- Lead – toxic to health and the environment.
- Diluted sulfuric acid – corrosive, can cause severe burns.
![]() What should you do with used batteries?
What should you do with used batteries?
Do not throw them in the trash!
Batteries and accumulators marked with the symbol below are subject to separate collection, so they must not be mixed with household waste:
Pb = Lead batteries
Take them to authorized collection points (recycling centers, stores that sell batteries).
Do not mix batteries with other types – this makes recycling more difficult.
The electrolyte (sulfuric acid) must be collected and neutralized only by authorized operators.
![]() Environmental impact
Environmental impact
Lead and sulfuric acid can contaminate soil and water.
Damaged batteries can release hydrogen — a flammable gas with an explosion risk.
Batteries are marked with recycling and warning symbols (corrosive, explosive, mandatory protection).
![]() Recommended personal protection
Recommended personal protection
If you handle used or damaged batteries:
Wear safety goggles, acid-resistant gloves, and protective clothing.
Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling.
Wash your hands after contact.
Store batteries in a dry, ventilated place, away from heat sources or open flame!
Do not store batteries in unattended places (near trash chutes or in other public areas). They are not only an environmental hazard, but also end up in improper recovery streams that can have unpredictable consequences for human health.
Do not open, puncture, or burn the battery!
Avoid contact with the liquid inside.
![]() Battery recycling – an efficient and sustainable solution
Battery recycling – an efficient and sustainable solution
Battery recycling, especially for lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, is one of the most promising and efficient forms of industrial recycling. It enables the recovery of valuable metals, helping reduce environmental impact and support the circular economy.
By recycling:
- Greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption are reduced.
- Risks associated with improper storage are avoided.
- Dependence on the extraction of natural resources is reduced.
Recycling is our responsibility!
Collection + Recovery of used batteries with Rombat = Resources for Romania
It is important that every user actively contributes to collecting and handing over used batteries at designated collection points.
Positive aspects of recycling used lead-acid batteries
Aspect
Benefit
![]() High recycling rate
High recycling rate
Over 95% of the material can be reused: lead, plastic, electrolyte
![]() Closed loop
Closed loop
Recycled lead can be used for new batteries, reducing mining extraction
![]() Reduced pollution risks
Reduced pollution risks
Recycling prevents environmental contamination with lead and sulfuric acid
![]() Reduced climate impact
Reduced climate impact
The energy required for recycling is lower than that for extracting ores


